Stay up-to-date with our latest news and learn more about local history!
NEWS
- Filter by
- Categories
- Tags
- Authors
- Show all
- All
- 20th amendment
- 23andme
- advice
- amusement parks
- ancestry
- archives
- artifacts
- bathing suits
- belinda springs
- Bellevue Asylum
- black history
- black history month
- christmas
- civil war
- collections
- dna
- Drinks
- exhibits
- family tree
- genealogy
- Gilded Age
- hagerstown
- Harry “Snap” McCoy
- history
- Horse thieving
- kee mar college
- kinship
- local history
- Miller House
- miller house museum
- moonshiner
- mourning
- museum
- news
- old film
- old photographs
- paintings
- pen mar park
- preservation
- prohibition
- Railroads
- Ransom of Hagerstown
- research
- row's amusement
- scrapbooks
- summer
- swim suits
- travel
- Updegraffs
- vacation
- Victorian
- washington county
- Washington County Black History
- washington county free library
- washington county hospital
- Western Maryland Black History
- western maryland railroad
- where is william
- whiskey and moonlight
- women's history
- women's history month
- women's rights
- women's suffrage
- world war i
- wrapping paper
July 14, 2024
Published by Zach Brooks at July 14, 2024
Categories
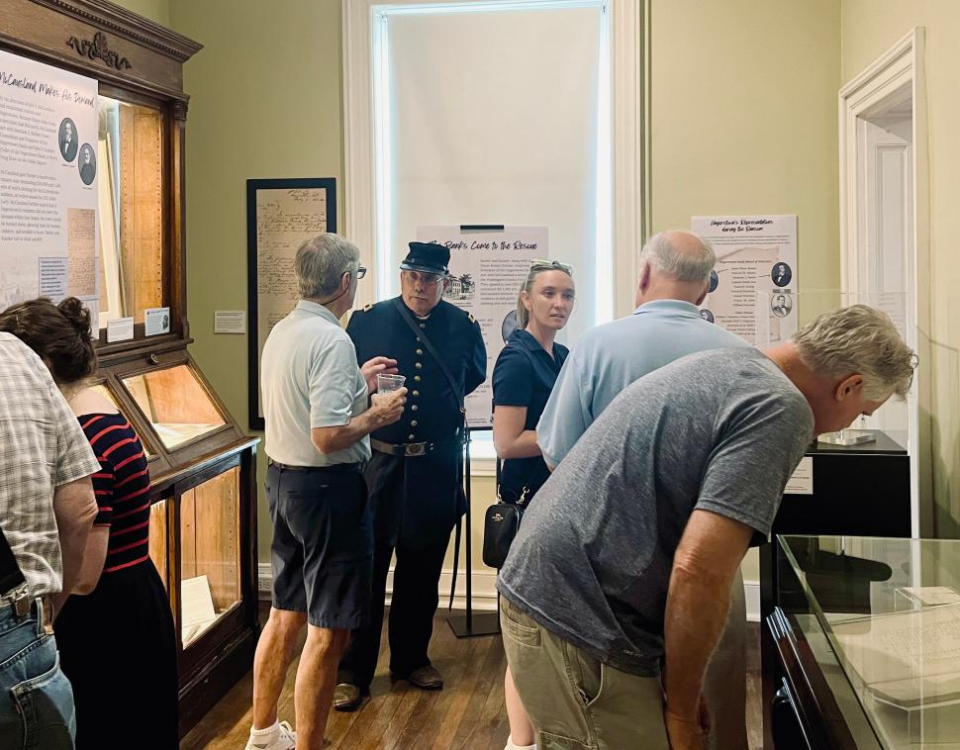
By Zach Brooks and Abigail Koontz There’s a new exhibit at the Miller House Museum in downtown Hagerstown that recalls one of the most dramatic incidents in the city’s history. As if July were not hot enough, in the summer of 1864, the fourth summer of the Civil War, Confederate Brig. Gen. John McCausland rode into town and demanded $20,000 and 1,500 sets of clothing for his cavalrymen. And if Hagerstown’s residents did not meet the demand within four hours, he promised to burn the whole town down. By the afternoon of July 6, McCausland — who was part of a Confederate contingent led by Lt. Gen. Jubal Early and bent on taking the war straight to Washington — had taken control of Hagerstown. Mayor John Cook, a merchant, had fled north. McCausland convened with Councilman Matthew S. Barber, who also was treasurer of the Hagerstown Bank, and bank teller John H. Kausler at Byer’s Drug Store in Public Square; and then again, joined by Hagerstown Bank president and former Congressman James Dixon Roman, at the Washington County Courthouse. They reached an agreement to raise the $20,000, though there was a dispute over the provision of 1,500 suits of clothes. Eventually, McCausland […]
June 17, 2024
Published by Zach Brooks at June 17, 2024
Categories
Article Author: Abigail Koontz (This article originally appeared on The Herald-Mail July, 2024) While American gangsters Al Capone and Bugs Moran were terrorizing Chicago, over 631 miles away in Washington County, local moonshiner Harry “Snap” McCoy was busy distilling and selling illegal liquor in Hagerstown and the surrounding communities. McCoy’s story captures the turbulent years of Prohibition and the history of moonshiners active in Washington County during that time. McCoy was born Jan. 7, 1870, to blacksmith Elbert McCoy and Emma (Ardinger) of Williamsport. In 1878, Elbert died of tuberculosis, leaving Emma to care for five children. McCoy’s childhood in Williamsport was a bustling, novel one. The Cumberland Valley Railroad reached the outskirts of Williamsport in 1872. The following year, the Western Maryland Railroad ran directly into Williamsport, connecting to the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal. The railroad had a profound effect on McCoy. Although he only completed the fourth grade, by age 30 he worked as a conductor for the WMRR in Williamsport. A 1906 photograph in the Washington County Historical Society collection captures McCoy posing for the camera beside his friend, Sam McClannahan, at the train station. An oncoming train is visible just over their shoulders. In January 1919, […]
May 21, 2024
Published by Robyn Sumner at May 21, 2024
Categories
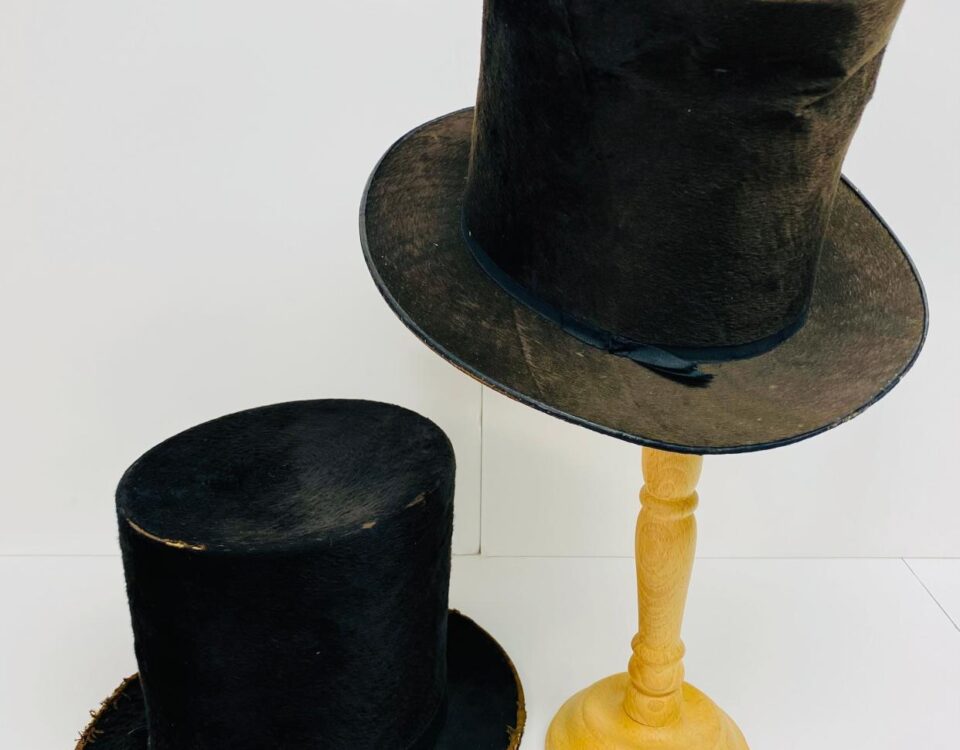
Article Author: Abigail Koontz (This article originally appeared on The Herald-Mail May, 2024) Hats have long fulfilled many roles, from functionality to symbols of self-expression and social status. One iconic hat of the last two centuries is the top hat. Two 19th-century silk top hats in the Washington County Historical Society’s collection offer glimpses into early local hat manufacturers — particularly the hatter George Updegraff. When top hats emerged in the 1790s, descending from earlier styles like the 17th century Pilgrim hat, they were made from felted beaver fur. Beaver felt top hats were initially expensive status symbols, but they were also functional, as beaver fur shed water. Beaver fur was so popular the European beaver population had been depleted by the mid-1600s. French fur traders sought beaver pelts in North America, trading with native populations for furs or hunting down beavers along rivers. Trappers moved further west, decimating beaver populations and spreading malaria through native populations, until reaching California by the 1820s. As pelts flooded American markets, the prevalence of American beaver felt top hats grew, influenced by European fashions. Washington County was no exception. On Aug. 12, 1823, the Maryland Herald announced that the hat manufacturing firm, Updegraff […]
April 25, 2024
Published by Zach Brooks at April 25, 2024
Categories
Article Author: Abigail Koontz (This article originally appeared on The Herald-Mail April, 2024) The American West between from 1865 to 1895 is often painted as the untamed, lawless domain of bandits and cowboys. But did you know that Western Maryland had its own bandits during that time? Across Washington County, residents of local towns, villages and farms were plagued by the relentless and crafty schemes of horse thieves. Western Maryland in the early 19th century saw the emergence of turnpikes, railroads and canals, but the most common means of transportation was by foot, horse or horse-drawn transport. Horsepower touched many aspects of daily life, from individual transport to income. Horses pulled barges, fire engines, mail coaches, farm equipment and hearses; they hauled resources and powered wars. Because horses were such a necessity, thieves saw a lucrative opportunity, especially in areas like Washington County that still were part of the frontier. Between 1790 and 1804, Washington County newspapers such as The Washington Spy and its successor, The Maryland Herald and Elizabeth-Town Advertiser, published more than 110 notices of horse theft (not counting lost horses). Victims during this time offered a range of monetary rewards for their horses and the capture of […]